On offset printing presses, there are various types of dampening systems. There is no strict classification of these types. For clarity, let’s try to group them based on different characteristics.
Classification of Dampening Systems in Printing Machines (Offset Printers)
Depending on the method of applying the solution to the plate, dampening systems in offset printers can be divided into three groups:
- Direct or Independent Dampening Systems – In these systems, the dampening and inking rollers are connected only through the plate cylinder. The solution is applied via dampening rollers.
- Non-Contact Dampening Systems – These systems apply the solution without direct roller contact, for example, by spraying through nozzles (Fuko systems) or by condensing steam on a cooled printing plate. Such systems are no longer used in modern machines.
- Integrated or Mixed Dampening Systems – These systems transfer the solution indirectly through the inking system. Their drawback is that excessive dampening causes the ink to emulsify quickly, requiring a full ink replacement to continue printing.
Classification Based on Roller Covering Material:
- Mollet dampening systems – Some rollers are covered with moisture-absorbing fabric.
- Non-fabric roller systems – These systems do not use cloth-covered rollers.
Classification Based on Solution Regulation and Supply Control:
- Intermittent dampening systems – Utilize an oscillating transfer roller.
- Continuous (film) dampening systems – Maintain a constant solution film.
There are many types of dampening systems. Some have long become obsolete, while others were only used in experimental models. We will not cover such rare systems but will focus on those commonly used in modern printing machines.
Dampening Systems in Printing Machines (Real Examples)
It is important to note that this overview does not aim to compare different types of printing equipment. There is no single criterion for evaluating dampening systems, and it would be a mistake to judge them based on the number of rollers (for instance, the more modern Heidelberg Speedmaster has fewer rollers than the GTO) or the type of roller covering (the more advanced Ryobi 500 series uses a molleton system, while the 3300 series features Crestline). Each system has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the design expertise of each manufacturer should not be underestimated.
Molleton Dampening System
This is the most traditional, time-tested, and classic dampening system, featuring fabric-covered rollers. Sometimes, it is even referred to as the “standard” system. Today, most offset printing machines are equipped with this type of dampening system.
Advantages:
- Affordable cost
- Widely recognized and familiar among offset printing professionals
- Easy to set up and provides stable dampening when the solution composition and operating techniques are properly maintained
There are several variations of this system, differing in the number, arrangement, and material of the rollers. The covers are typically made of knitted or woven fabric. Recently, synthetic heat-shrinkable covers have become popular.
Key benefits of synthetic covers:
- Seamless design
- No dust or lint
- Slightly larger diameter that shrinks to fit when treated with hot water
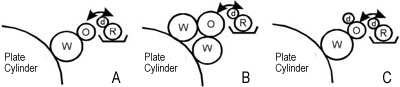
In Figure 1, the main configurations of the molleton dampening system are shown.
The simplest scheme (Figure A) consists of four rollers, including one form roller (in contact with the printing plate). Such dampening units are installed on Multigraphics, Hamada, and Ryobi 3200MCD machines.
A system containing five rollers, two of which are form rollers (Figure B), can be found on Dominant, Polly, Hamada series C, B, and A, as well as Ryobi 500 series machines.
A different system is used in Ryobi 3300MR, 3302M, and Itek 3985 machines (Figure 1C). This system also employs five rollers, but only one of them is a form roller. Let’s take a closer look at the molleton system using this example. The ductor roller (R) and oscillating roller (O) (which move back and forth along their axis) have a chrome coating, while the transfer roller (S), intermediate roller (D), and form roller (W) are covered with knitted fabric sleeves.
For stable water supply, the transfer roller moves cyclically, alternately contacting the ductor roller, which is immersed in a special solution reservoir, and the oscillating roller. By fixing this roller in one position, the solution supply can be stopped. Solution metering is carried out either by changing the rotation speed of the ductor roller (if it has a separate drive) or by adjusting its single-turn angle (if driven by a ratchet mechanism).
The relative positioning of the rollers in the dampening unit is crucial for stable operation. To ensure even and continuous supply of dampening solution, the pressure between rollers should increase as the solution moves from the ductor roller to the plate cylinder. Although a press operator can adjust this, ideally, a professional technician should handle it. A paper strip (80 g/m²) is used for checking pressure by assessing the force required to pull the strip from between wet rollers without tearing it. Metallic or plastic feeler gauges are less effective, as their resistance depends not only on pressure but also on surface condition, humidity, etc. The maximum pressure should be at the contact point of the rollers with the printing plate. Each printing press model has its specific adjustment mechanisms.
The main disadvantage of molleton systems is their labor-intensive maintenance. However, this can be mitigated by using modern synthetic sleeves and strictly following technological guidelines.
Dahlgren System
The Dahlgren company is one of the pioneers of continuous dampening systems.
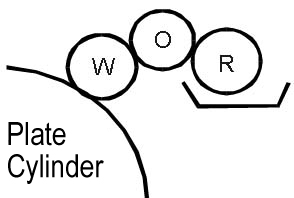
The indirect dampening unit (Figure 2) consists of only three rollers:
- A rubber ductor roller
- A chrome-plated form cylinder
- An intermediate rubber roller, which also serves as a common roller for both the inking and dampening systems
The amount of dampening solution supplied is regulated by adjusting the speed of the ductor and intermediate rollers, which have independent drives.
Disadvantages of the Dahlgren System:
- Fewer rollers, which can lead to greater unevenness in solution distribution across the width of the printing plate.
- No pre-wetting mode for the plate, meaning that when the press starts, the printing plate is immediately inked. To prevent this, operators must manually pre-wet the plate before starting the machine.
Aquamagic System
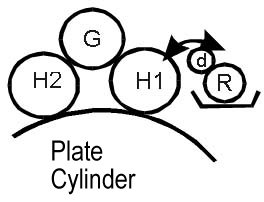
The Aquamagic system is an alcohol-based dampening system (Figure 3) developed by Ryobi. Unlike the Dahlgren system, it features four rollers and intermittent solution feed.
Key Features:
- All rollers, except the ductor roller, rotate at the same speed as the press.
- One roller moves along its axis, ensuring even solution distribution across the width of the plate.
- The amount of dampening solution is controlled by adjusting the speed of the ductor roller.
- Solution flow can be temporarily stopped by locking the transfer roller.
Aquamatic System
The Aquamatic system is an alcohol-based dampening system (Figure 4) used on printing presses by the AV Dick company.
Key Features:
- Unlike previous systems, the contact between the dampening apparatus and the ink roller occurs earlier.
- The transfer oscillating roller touches the ductor dampening roller on one side and the ink roller on the other side.
- As a result, the number of dampening rollers is lower compared to the previous system, and two rollers work for both systems simultaneously.
- The water-ink balance starts to establish earlier, which is a positive aspect.
- However, this system has a greater tendency toward emulsification.
- The amount of dampening solution is regulated by adjusting the speed of the ductor roller.
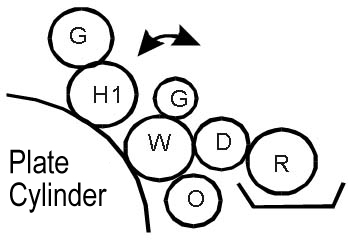
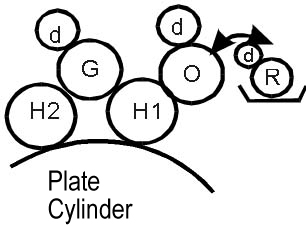
Despite its apparent simplicity, this film dampening system (Figure 5) is the latest development by Heidelberg.
Key Features:
- The processes of pre-inking on the dampening rollers, plate wetting, and dampening apparatus cleaning are fully automated.
- The system includes four dampening rollers: ductor (R), metering (S), inked (W), and spread (O) rollers.
- The inked roller is always in contact with the ink system.
- According to the manufacturers, computer modeling was used during the creation of this system, and the optimal configuration was chosen.
Crestline System
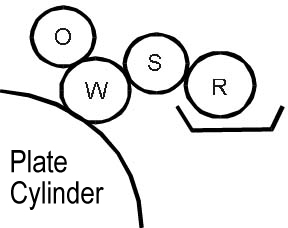
This is a direct film dampening system (Figure 6). In this system, the dampening rollers do not come into contact with the ink rollers, allowing for independent supply of water and ink.
Key Features:
- Self-regulating system: When the ink supply increases sharply, the dampening solution supply automatically increases, preventing ink from rolling onto blank areas of the plate.
- This system saves time for the printer, allowing them to focus on more important tasks.
- The manual adjustment option is also available, allowing the water supply to be regulated by adjusting the gaps between the rollers.
- This original system is used on Ryobi 3300CR, 3302C, Itek 3980, and is sometimes installed on machines like AV Dick, Hamada, Multi, Toko, and Heidelberg GTO.
Other Dampening Systems for Printing Presses
The list of dampening systems is not exhaustive with the ones discussed in this article. For example, here is a list of names of some other systems:
- Alcomatic, Aquafine, Eric, Rolandmatic, Ryobimatic, Ryobi SuperDampener, Komori-matik, Miehlermatic, Varn Kompac, and many others without specific names.
Almost every major printing equipment manufacturer develops unique dampening devices or makes modifications to previously used systems.
Adjusting Roller Position in Systems Without Fabric Coatings
In systems without fabric-coated rollers, as a rule, there is no externally accessible adjustment handle for changing the pressure of the dampening roller on the plate, as seen in Molleton-based systems. This suggests that there are stricter requirements for the relative positioning of the rollers, and it is preferable for a qualified technician to perform these adjustments.
However, a few words about these settings:
- For such checks, standard gauge strip testing is not sufficient.
- The pressure is checked by the contact stripes left by the rollers coated with ink.
- It is necessary that these stripes are of uniform width (not wedge-shaped) and that for rollers closer to the plate, the stripe width should be no smaller than those of the previous rollers.
Specific values of these stripes vary across different printing press models (for example, in the Crestline system, the following values apply: pressure on the plate = 4.5 mm, and between the other rollers = 4 mm).
Maintenance of Dampening Units (Dampening Devices for Printing Presses)
Now, let’s talk about the maintenance of dampening devices. It is not recommended to use strong chemicals designed for ink systems to clean the rollers from dried ink. If a lot of ink has accumulated on the rollers during printing, it is better to remove it using a cloth soaked in dampening solution or an alcohol-based additive, rather than a solvent-based cleaner like kerosene. In general, it is preferable to avoid using such solvents and opt for water-soluble chemicals. The principle behind these liquids is based on breaking down printing inks, after which the rollers can be easily cleaned with regular water.
After cleaning the dampening system, the rollers should be treated with special preservatives to soften and protect them. For chromed rollers, it is also advisable to use appropriate chemicals. The condition of the roller surfaces, their hardness, and elasticity are of great importance. There have been cases where roller defects could not be determined visually, and only after replacing them did the machine start functioning properly.
